本文部分内容节选自Java Guide, 地址: https://javaguide.cn/java/collection/java-collection-questions-01.html
🚀 基础(上) → 🚀 基础(中) → 🚀基础(下) → 🤩集合(上) → 🤩集合(下) → 🤗JVM专题1 → 🤗JVM专题2 → 🤗JVM专题3 → 🤗JVM专题4 →😋JUC专题1 → 😋JUC专题2
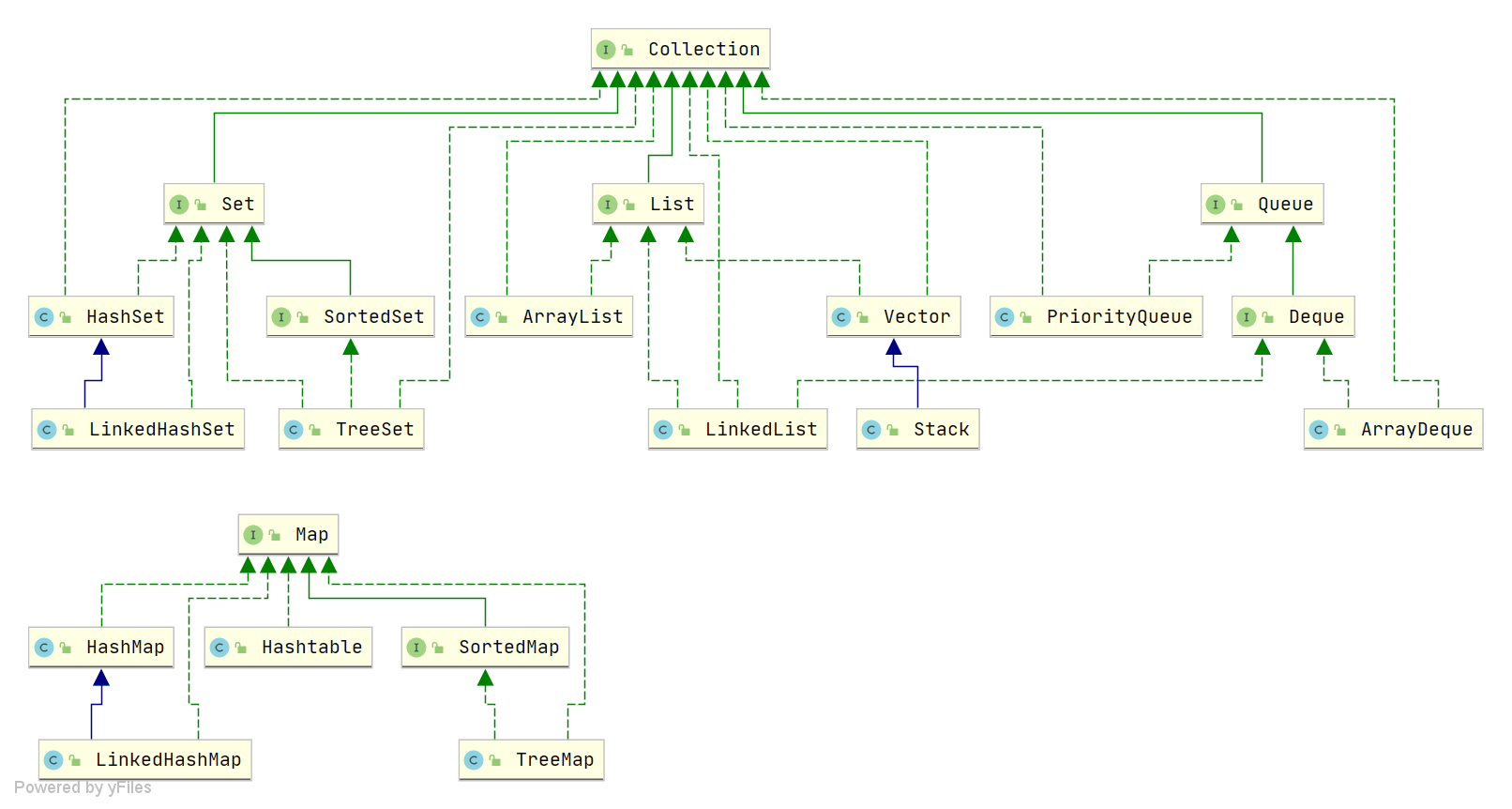
Java 集合概述 Java 集合, 也叫做容器, 主要是由两大类接口派生而来, 一个是 Collection 接口, 主要用于存放单一元素; 另一个是 Map 接口, 主要用于存放键值对. 对于 Collection , 下面又有三个主要的子接口 List , Set 和 Queue
Java 集合框架如下所示:
说说 List, Set, Queue, Map 四者的区别? List : 存储的元素是有序的可重复的Set : 存储的元素是不可重复的Queue : 队列. 存储元素是可重复的, 有序的Map : 使用键值对(key-value)存储, 类似于数学上的函数 y=f(x), “x” 代表 key, “y” 代表 value, key 是无序的, 不可重复的, value 是无序的, 可重复的, 每个键最多映射到一个值List ArrayListArrayList 是 Object[] 数组, 底层是数组数列, 相当于动态数组. 与 Java 的数组相比, 它的容量可以动态增长. 在添加大量元素前, 应用程序可以使用ensureCapacity操作来增加 ArrayList 实例的容量. 这可以减少递增式再分配的数量
如果你有学过C++的话, 你应该会意识到 ArrayList 和 C++ 中的 Vector 非常相似. Vector 也是动态数组, 也能动态增长.
ArrayList 继承于 AbstractList , 实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable 这些接口
List 表明它是一个列表, 支持添加, 删除, 查找等操作, 并且可以通过下标进行访问RandomAccess 表明实现这个接口的 List 是支持快速访问的. 在 ArrayList 中, 我们可以通过元素的下标来直接获取元素, 这就是快速访问Cloneable 表明它具有拷贝能力, 可以进行深拷贝和浅拷贝操作Serializable 表明它可以序列化, 也就是可以把对象转换为字节流进行存储或进行网络传输ArrayList 可以存储任何类型的对象, 但是不建议存储 null 值, 因为一方面 null 值没有意义, 另一方面存储 null 值可能会导致空指针异常
ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的区别?线程安全 : ArrayList 和 LinkedList 都是不同步的, 也就是不保证线程安全底层数据结构 : ArrayList 底层使用的是 Object 数组, LinkedList 底层使用的是双向链表插入与删除 :ArrayList 采用数组存储, 所以插入和删除元素受元素个数影响. 例如, 执行 add(E e) 方法时, ArrayList 会默认将元素插入到末尾, 时间复杂度就是O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) add(int index, E e) , 时间复杂度就是O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) LinkedList 采用链表存储, 所以在头尾插入删除元素不受元素个数影响, 时间复杂度为O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) add(E e) , addFirst(E e) , addLast(E e) , removeFirst() , removeLast()). 但是如果在指定位置插入或删除元素 (如 add(int index, E e) , remove(Object o) , remove(int index)) , 时间复杂度就是O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) 快速随机访问 : LinkedList 不支持快速随机访问内存占用 : ArrayList 的内存浪费体现在 ArrayList 的末尾会预留空间, 而 LinkedList 的内存浪费体现在 LinkedList 的每个元素都要有一个前驱指针和一个后缀指针ArrayList 核心源码public class ArrayList <E> extends AbstractList <E> implements List <E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L ; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 ; private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; transient Object[] elementData; private int size; public ArrayList (int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0 ) { this .elementData = new Object [initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0 ) { this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity); } } public ArrayList () { this .elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } public ArrayList (Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0 ) { if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { this .elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } } public void trimToSize () { modCount++; if (size < elementData.length) { elementData = (size == 0 ) ? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA : Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } } public void ensureCapacity (int minCapacity) { int minExpand = (elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) ? 0 : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; if (minCapacity > minExpand) { ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); } } private static int calculateCapacity (Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } private void ensureCapacityInternal (int minCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } private void ensureExplicitCapacity (int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0 ) grow(minCapacity); } private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8 ; private void grow (int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1 ); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0 ) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0 ) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity (int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0 ) throw new OutOfMemoryError (); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } public int size () { return size; } public boolean isEmpty () { return size == 0 ; } public boolean contains (Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0 ; } public int indexOf (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i] == null ) return i; } else { for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1 ; } public int lastIndexOf (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int i = size - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (elementData[i] == null ) return i; } else { for (int i = size - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1 ; } public Object clone () { try { ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super .clone(); v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); v.modCount = 0 ; return v; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { throw new InternalError (e); } } public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { if (a.length < size) return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass()); System.arraycopy(elementData, 0 , a, 0 , size); if (a.length > size) a[size] = null ; return a; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E elementData (int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; } public E get (int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } public E set (int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } public boolean add (E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); elementData[size++] = e; return true ; } public void add (int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1 ); System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1 , size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } public E remove (int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1 , elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; return oldValue; } public boolean remove (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null ) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } else { for (int index = 0 ; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true ; } } return false ; } private void fastRemove (int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1 ; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1 , elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null ; } public void clear () { modCount++; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null ; size = 0 ; } public boolean addAll (Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); System.arraycopy(a, 0 , elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0 ; } public boolean addAll (int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0 ) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); System.arraycopy(a, 0 , elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0 ; } protected void removeRange (int fromIndex, int toIndex) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - toIndex; System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex, numMoved); int newSize = size - (toIndex - fromIndex); for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) { elementData[i] = null ; } size = newSize; } private void rangeCheck (int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private void rangeCheckForAdd (int index) { if (index > size || index < 0 ) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException (outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private String outOfBoundsMsg (int index) { return "Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size; } public boolean removeAll (Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, false ); } public boolean retainAll (Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, true ); } public ListIterator<E> listIterator (int index) { if (index < 0 || index > size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException ("Index: " + index); return new ListItr (index); } public ListIterator<E> listIterator () { return new ListItr (0 ); } public Iterator<E> iterator () { return new Itr (); }
ArrayList 扩容机制根据上面的源码, 我们可以确定的一个事实是: 当以无参数构造方法构造一个新的 ArrayList 时, 实际上初始化赋值的是一个空数组, 只有插入一个新元素的时候, ArrayList 的容量才会扩容到10
初始扩容后, 容量一次扩张到10, 之后每次扩容都会将容量扩张到原来的1.5倍
举个例子, 给一个空 ArrayList 添加一个元素, ArrayList 发生第一次扩容, 此时 ArrayList 的容量变为 10. 之后添加第2, 3, … 9, 10个元素, 都不会再扩容了. 直到添加第11个元素, 容量不足, ArrayList 自动扩容, 扩容到原来的 1.5 倍, 容量变为15. 这里注意, 如果原来的容量是奇数, 那么原容量乘以1.5会出现小数, 实际上扩容会把小数位丢掉.
(如果你有学过C++的话, 可以拿 ArrayList 的扩容机制和 Vector 的扩容机制做个对比, 总体来讲还是比较相似的)
在扩容之后, 根据上面的源码, 我们可知: 如果新容量大于 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE , 就会执行 hugeCapacity() 方法比较 minCapacity 和 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE, 如果 minCapacity 大于 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE , 那么新容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE , 否则, 新容量大小为 Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8
扩容的本质是新建一个更大的 ArrayList , 然后将老的 ArrayList 的元素拷贝到新的 ArrayList . 拷贝有两个方法: Arrays.copyOf() 和 System.arraycopy() . 根据上面的源码可知, Arrays.copyOf() 实际上调用了 System.arraycopy() . 但两者存在区别, arraycopy() 需要目标数组, 将原数组拷贝到目标数组(重新定义的数组或者原数组), 可以选择拷贝的起点和长度以及放到目标数组的位置. copyOf() 是新建一个数组, 拷贝完成以后返回新数组
Vector底层实现为Object[] 数组
LinkedList底层实现为双向链表
LinkedList 插入删除的时间复杂度?头部插入/删除, 尾部插入/删除:O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) 除了头尾部的插入/删除:O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) LinkedList 为什么不能实现 RandomAccess ?LinkedList 的底层数据结构是链表, 而链表中元素的内存位置不一定是连续的, 只能依赖于指针进行定位, 所以不能实现 RandomAccesss
LinkedList 源码分析public class LinkedList <E> extends AbstractSequentialList <E> implements List <E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { }
以上是 LinkedList 的类定义
由代码可知, LinkedList 继承了 AbstractSequentialList , 实现了 List , Deque , Cloneable , Serializable 接口
List : 表明它是一个列表Deque : 继承自 Queue , 表明它具有双端插入/删除的特性Cloneable : 表明它具有拷贝能力, 可以进行深拷贝和浅拷贝操作Serializable : 表明它可以序列化, 也就是可以把对象转换为字节流进行存储或进行网络传输LinkedList 中的元素是通过 Node 定义的
private static class Node <E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this .item = element; this .next = next; this .prev = prev; } }
以下是 LinkedList 的构造函数
public LinkedList () {} public LinkedList (Collection<? extends E> c) { this (); addAll(c); }
插入元素使用 add() 方法. add() 方法有两个版本
add(E e) , 将元素添加到 LinkedList 的末尾, 时间复杂度为 O(1)add(int index, E e) , 将元素添加到指定位置. 这需要先查找到对应位置, 然后再插入. 时间复杂度为O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) public boolean add (E e) { linkLast(e); return true ; } public void add (int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); } void linkLast (E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node <>(l, e, null ); last = newNode; if (l == null ) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } void linkBefore (E e, Node<E> succ) { final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node <>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null ) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
获取元素有三个函数, getFirst() , getLast() , get(int index)
getFirst() : 获取链表的头节点元素, 时间复杂度O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) getLast() : 获取链表的尾节点元素, 时间复杂度O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) get(int index) : 获取指定位置元素, 时间复杂度O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) public E getFirst () { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null ) throw new NoSuchElementException (); return f.item; } public E getLast () { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null ) throw new NoSuchElementException (); return l.item; } public E get (int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; }
这里的核心在于下面这一段源码
Node<E> node (int index) { if (index < (size >> 1 )) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0 ; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1 ; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
get(int index) 和 remove(int index) 都调用了这个方法来获取指定位置的节点
删除元素有5个方法, removeFirst() , removeLast() , remove(E e) , remove(int index) , clear()
removeFirst() : 删除头节点. 时间复杂度O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) removeLast() : 删除尾节点. 时间复杂度O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) remove(E e) : 删除链表中首次出现的指定元素, 如果不存在就返回 false. 时间复杂度O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) remove(int index) : 删除链表中指定位置的元素. 时间复杂度O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) clear() : 删除链表中全部元素. 时间复杂度O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) public E removeFirst () { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null ) throw new NoSuchElementException (); return unlinkFirst(f); } public E removeLast () { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null ) throw new NoSuchElementException (); return unlinkLast(l); } public boolean remove (Object o) { if (o == null ) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null ; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null ) { unlink(x); return true ; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null ; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true ; } } } return false ; } public E remove (int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); }
这里的核心在于 unlink() 方法
E unlink (Node<E> x) { final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null ) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null ; } if (next == null ) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null ; } x.item = null ; size--; modCount++; return element; }
unlink() 的逻辑如下
首先获取待删除节点 x 的前驱和后继节点. 判断待删除结点是否为头结点或尾节点如果 x 是头节点, 则将 first 指向 x 的后继节点 如果 x 是尾节点, 则将 last 指向 x 的前驱节点 如果 x 不是头节点也不是尾节点, 则进行下一步操作 将待删除节点的前驱节点的后继指向待删除节点的后继节点, 断开 x 和 x.prev 的连接 将待删除结点的后继节点的前驱指向待删除节点的前驱节点, 断开 x 和 x.next 的连接 将待删除节点 x 的元素置空, 修改链表长度 关于遍历 LinkedList , 推荐使用 for-each 进行遍历
LinkedList<String> list; list.add("Yonagi" ); list.add("Hello" ); list.add("World" ); for (String s : list) { System.out.println(s); }
LinkedList 遍历的核心其实是它的迭代器
private class ListItr implements ListIterator <E> { private Node<E> lastReturned; private Node<E> next; private int nextIndex; private int expectedModCount = modCount; ………… }
头到尾方向的迭代
public boolean hasNext () { return nextIndex < size; } public E next () { checkForComodification(); if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException (); lastReturned = next; next = next.next; nextIndex++; return lastReturned.item; }
尾到头方向的迭代
public boolean hasPrevious () { return nextIndex > 0 ; } public E previous () { checkForComodification(); if (!hasPrevious()) throw new NoSuchElementException (); lastReturned = next = (next == null ) ? last : next.prev; nextIndex--; return lastReturned.item; }
Set Comparable 和 Comparator 的区别 Comparable 和 Comparator 接口都是 Java 中常见的用于排序的接口
Comparable 接口实际上是出自 java.lang 包, 它有一个 compareTo(Object obj) 方法用于排序Comparator 接口实际上出自 java.util 包, 它有一个 compare(Object object1, Object object2) 方法用于排序无序性和不可重复性的含义是什么 无序性是指存储的数据在底层数组中排列的顺序并非是按照数组索引增加进行排序, 而是根据哈希值进行排序 不可重复性是指添加元素通过 equals() 判断时, 返回 false. 比较 HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet HashSet , LinkedHashSet 和 TreeSet 都是接口 Set 的实现类, 都能保证元素的不可重复性, 且能保证线程安全HashSet , LinkedHashSet 和 TreeSet 的区别在于底层数据结构的不同. HashSet 是底层是哈希表 (基于 HashMap ); LinkedList 的底层是链表和哈希表, 且元素插入取出满足FIFO; TreeSet 的底层是红黑树, 元素是有序的, 排序的方式有自然排序和定制排序底层数据结构的不同又导致它们的应用场景不同. HashSet 用于不需要保证元素插入和取出顺序的场景, LinkedHashSet 用于保证元素的插入和取出顺序满足 FIFO 的场景, TreeSet 用于支持对元素自定义排序规则的场景 Queue Queue 和 Deque 的区别 Queue 是单端队列, 只能在一端插入元素, 在另一端删除元素
Queue 实现了 Collection 的接口, 根据容量问题而导致操作失败处理的不同, 分为两类: 一类是操作失败后抛出异常, 一类是操作失败后返回特殊值
Queue 接口抛出异常 返回特殊值 插入队尾 add(E e) offer(E e) 删除队头 remove() poll() 查询队头元素 element() peek()
(说说我个人的喜好, 我个人更喜欢用返回特殊值类型的方法, 抛出异常的方法就我个人而言, 无论是写题还是写项目代码都很少用到)
Deque 是双端队列, 在队头队尾都能插入删除
Deque 实现了 Queue 的接口, 增加了在队头插入/队尾删除的方法. 和 Queue 通用, Deque 根据容量问题而导致操作失败处理的不同, 也分为两类: 一类是操作失败后抛出异常, 一类是操作失败后返回特殊值
Deque 接口抛出异常 返回特殊值 插入队头 addFirst(E e) offerFirst(E e) 插入队尾 addLast(E e) offerLast(E e) 删除队头 removeFirst() pollFirst() 删除队尾 removeLast() pollLast() 查询队头元素 getFirst() peekFirst() 查询队尾元素 getLast() peekLast()
实际上, Deque 还有 push() 和 pop() 方法, 用于模拟栈
ArrayDeque 与 LinkedList 的区别 ArrayDeque 是基于可变长的数组和双指针来实现, 而 LinkedList 是基于链表实现ArrayDeque 不支持存储 NULL 数据, 而 LinkedList 支持ArrayDeque 插入时可能存在扩容过程, 均摊后时间复杂度为O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) LinkedList 虽不需要扩容, 但是每次插入数据时都需要申请新的空间, 均摊后性能更差PriorityQueuePriorityQueue 利用了二叉堆的数据结构来实现, 底层使用可变长的数组来存储元素PriorityQueue 通过堆元素的上浮和下沉, 实现了在O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n ) PriorityQueue 是非线程安全的, 且不支持存储 NULL 值和 non-comparable 对象PriorityQueue 默认是小根堆, 但是可以接收一个 Comparator 作为构造参数, 自定义元素优先级BlockingQueueBlockingQueue 是一个接口, 继承自 Queue . BlockingQueue 阻塞的原因是当队列内没有元素的时候会一直阻塞, 直到有元素; 如果队列已满, 会等到队列有空间了再放入
BlockingQueue 常用于生产者-消费者模型
BlockingQueue 的实现类有哪些? ArrayBlockingQueue : 使用数组实现的有界阻塞队列. 创建时需要指定容量大小, 并且支持公平和非公平两种方式的锁访问机制LinkedBlockingQueue : 使用单向链表实现的可选有界阻塞队列, 在创建时可以指定容量, 如果不指定容量则默认为 Integer.MAX_VALUE . 和 ArrayBlockingQueue 一样, 支持公平和非公平两种方式的锁访问机制PriorityBlockingQueue : 支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列. 元素必须支持 comparable 或者在构造时指定 Comparator . 不支持插入 NULL 值SynchronousQueue : 同步队列, 是一种不能存储元素的阻塞队列, 每个插入操作必须等待一个删除操作, 同理删除操作必须等待插入操作DelayQueue : 延迟队列, 里面的元素只有经过了指定的延迟时间, 才能出队ArrayBlockingQueue 和 LinkedBlockingQueue 的区别? ArrayBlockingQueue 基于数组实现; LinkedBlockingQueue 基于单向链表实现
ArrayBlockingQueue 是有界的, 且创建时必须指定大小; LinkedBlockingQueue 是可选有界的, 创建时可以选择指定大小, 如果不指定则默认为 Integer.MAX_VALUE
ArrayBlockingQueue 的锁是没有分离的, 也就是生产和消费都用的同一个锁; LinkedBlockingQueue 的锁是分离的, 生产和消费各有一个锁, 避免了消费者线程和生产者线程的锁争夺
ArrayBlockingQueue 需要提前分配内存, 而 LinkedBlockingQueue 则是插入元素时申请新的内存空间